Fast Grants
In order to mobilize Cornell to support ambitious climate action in this decisive decade, Cornell Atkinson and The 2030 Project: A Cornell Climate Initiative issue special requests for proposals for fast grant research-to-impact seed funding. We enable faculty to seize urgent and unique opportunities to provide support for impact-oriented climate research.
How to Apply
Eligibility:
- All PIs and CoPIs must meet Cornell’s principal investigator (PI) eligibility criteria
The 2025 “AI & Climate” Cycle is Closed
- Previous Request for Proposals
Questions or More Info:
2030 Fast Grant Awards
2025
Harnessing AI to Strengthen Nature’s Defense Against Climate Change: Forest Integrity in Cambodia

Nature’s capacity to buffer climate impacts depends on the ecological integrity of ecosystems. High-integrity forests store more carbon, support higher levels of biodiversity, and provide climate refuge for both people and nature. But current global indicators fail to capture ecological integrity in a way that can inform climate adaptation policy. Researchers will develop and test a framework that integrates diverse ecological data streams, including bioacoustics and camera trap data, remote sensing, AI-derived canopy maps, and threat monitoring (e.g., hunting, deforestation) to generate robust, dynamic indicators of ecological integrity, and provide wildlife managers with tools to target protection and monitoring priorities. The framework will be tested in Keo Seima Wildlife Sanctuary in Cambodia, a biodiversity-rich stronghold managed by the Wildlife Conservation Society.
Investigator: Dena Clink, Cornell Lab of Ornithology
Low-Cost Active Climate Monitoring with Underactuated Agents

Atmosphere and ocean data improve our understanding of the climate, but nature-based sampling can be expensive. Tools like weather balloons and ocean buoys are low-cost solutions, but they are fundamentally underactuated—meaning, they rely on underlying flows in the water or air to navigate. This project will develop planning and learning algorithms for measuring uncertain flows with underactuated agents, enabling active data gathering for critical regions. The project will also serve to deepen a partnership between researchers at Cornell and WindBorne Systems, an advanced weather balloon start-up, and to initiate a relationship with the Naval Research Laboratory.
Investigators: Sarah Dean, Cornell Bowers Computing and Information Science; Alexander Terenin, Center for Data Science for Enterprise and Society
The Green Choice: Enabling Sustainable Generative AI through Flexible System Co-Design

The exponential growth of Generative AI poses a critical sustainability challenge, driving unprecedented energy consumption and carbon emissions that threaten to destabilize power grids. Current AI services operate on rigid performance tiers, ignoring a crucial opportunity: user willingness to trade small delays in response time for a significantly lower environmental impact. This project introduces a user-guided co-design approach to create sustainable AI. Researchers will first develop EcoGPT, a tool for conducting large-scale user studies to quantify preferences for “green AI.” Building on these insights, they will design and implement FlexLLM, a novel run-time scheduler that leverages this user flexibility to dynamically map AI tasks across diverse hardware — from cutting-edge GPUs to older, more energy-efficient processors. This work will directly reduce AI’s carbon footprint, enable data centers to become flexible partners for the power grid, and provide the first data-driven framework for creating truly sustainable AI services.
Investigator: Udit Gupta, Cornell Tech and Cornell Engineering
AI-Enabled Synthesis of Bespoke Unconventional Solar-cell Materials

The vast majority of solar infrastructure relies on silicon solar cells. However, alternative materials like lead-halide perovskites are comparatively more defect tolerant and are estimated to cost less than quarter as much to produce. More than a dozen companies in the U.S. are currently pursuing perovskite commercialization. This project seeks to use artificial intelligence and machine learning to accelerate the translation of lead-halide perovskite solar cell materials from the lab to the factory. This project builds on two recent breakthroughs at Cornell. The first, by the teams of John Marohn and Roger Loring in Chemistry and Chemical Biology, is the invention of unique scanning-probe metrology tools for quantifying the electronic and ionic conductivity, charge density, and dielectric constant of thin semiconductor films. The second breakthrough, by Michael Lawler’s team in Physics, is the application of large-language models to optimize the growth of materials. In this project, researchers will carry out proof-of-concept experiments demonstrating that Lawler’s novel transformer-models enable the synthesis of lead-halide perovskite films with good film coverage, large grains, and, for the first time, well-controlled and reproducible ionic and electronic conductivity.
Investigators: John Marohn and Michael Lawler, both Arts & Sciences
AI-Powered Confidence in Additive Construction
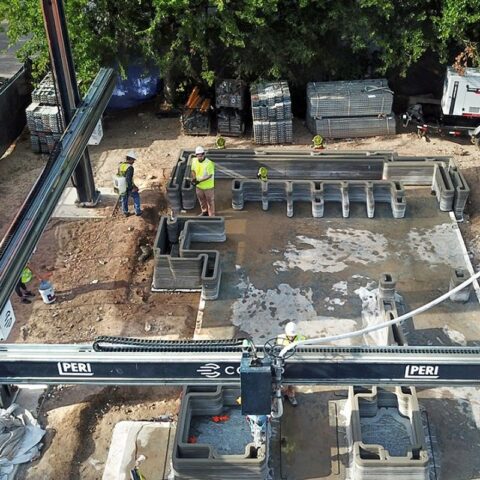

Additive construction, especially 3D concrete printing, is poised to positively impact the construction industry by reducing carbon in building and other construction, protecting people and infrastructure with building materials resistant to extreme events, and providing an avenue for rapid, automated, dignified housing for climate-displaced communities in transition. However, this relatively new construction technique faces key challenges: construction with extruded, layered cementitious materials introduces structural uncertainties at each layer interface, where the fabrication environment and layer-to-layer print times introduce variables in the way the layers bond. Researchers seek to collect camera and laser-line data that is synchronized with the relevant print processes and component geometry, and to employ machine learning to correlate print data to performance of the 3D printed elements. The key goal is to improve engineering confidence in the structural components fabricated using 3D concrete printing.
Investigators: Sriramya Nair and Nils Napp, both Cornell Engineering
AI-Enabled Robotic eDNA Sampling of Waterways

Climate change is rapidly altering freshwater ecosystems, yet early detection of species loss, range shifts, or invasive introductions remains difficult. Environmental DNA (eDNA) sampling offers unmatched sensitivity but is highly susceptible to contamination, undermining reliability and inflating costs. While autonomous robotic samplers excel at clean, consistent spatio-temporal sampling, they are prohibitively complex for field ecologists to operate and debug in the field. This project pairs autonomous unmanned surface vehicles (USVs) with an AI-driven conversational interface to enable clean, large-scale eDNA sampling by field ecologists, in turn boosting detection probabilities for emerging environmental problems.
Investigators: Kirstin Petersen, Cornell Engineering; Peter McIntyre, Cornell CALS
Motivating Climate Action Using Human-AI Dialogues

Climate change skepticism and inaction remain major barriers to collective climate action, with traditional static messaging showing little impact on either beliefs or behaviors. Building on evidence that adaptive large language model (LLM) dialogues can durably reduce conspiracy beliefs and climate doubts, this project proposes a new wave of experiments to understand and improve their effectiveness. We will examine why LLM dialogues shift some climate doubts more effectively than others, and why effects on specific concerns surpass broader beliefs and policy support. The research will integrate deeper elicitation of participants’ mental models of climate change, enabling tailored dialogues that target underlying doubts. We will also harness LLM adaptability to create individualized measures of climate action (e.g., contacting elected representatives), allowing direct assessment of behavioral impact. In parallel, we will test strategies for promoting public uptake of the intervention, including survey and field experiments with social media and search ads.
Investigators: David Rand, SC Johnson College of Business, Cornell Bowers Computing and Information Science, and Arts & Sciences; Gordon Pennycook, Arts & Sciences
Resilience Scanner: Leveraging AI to Accelerate Global Adoption of Municipal Climate Adaptation Technologies

AI has tremendous potential to amplify municipal investments in climate adaptation and resilience solutions. However, information about available and deployed technology-enabled adaptation and resilience solutions is scattered, incomplete, and out of date. As a result, many city leaders are unaware of solutions being implemented elsewhere, and many investors and innovators are unaware of potential markets for their solutions. To fill this gap, Townsend will create a comprehensive global source of knowledge about technology-enabled climate adaptation and resilience (A&R) solutions at the municipal level. Four key project goals are to: (1) highlight the potential for AI to amplify ongoing and planned investments, (2) cross-fertilize existing A&R technologies across cities, (3) identify areas of strong demand to strengthen the case for private sector investment, (4) identify gaps in the innovation system that can be addressed through philanthropic investment.
Investigator: Anthony Townsend, Cornell Tech
2024
Novel Polymer Membranes to Accelerate Green Hydrogen Technologies

Green hydrogen is created by using wind or solar power to generate electricity, which is then used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The resulting “green hydrogen” can be used in fuel cells to generate energy or to store energy, which can help compensate for the intermittent nature of wind and solar. This project seeks to develop new polymer membranes that will improve stability and conductivity in green hydrogen technologies.
Investigator: Geoffrey Coates, Chemistry and Chemical Biology
Meeting Cornell and NY Zero Carbon Energy Goals With Tidal Energy

Cornell researchers are partnering with At-Sea Development, a private company working to build a 100-megawatt tidal energy project in Long Island Sound, NY. When built, the project would deliver clean energy to New York City and downstate New York, where energy is currently 95% fossil fuel-based.
Investigators: Edwin (Todd) Cowen, Civil and Environmental Engineering; Seth Schweitzer, Civil and Environmental Engineering
Design and Testing of Novel Wave Energy Converter Farms

Cornell researchers are partnering with colleagues at Oregon State University to improve conversion of wave energy into power production. Oregon State began construction this summer of a new wave energy testing facility off the coast of Newport, OR. One of the key project aims is to develop and test innovative designs that can pull energy from multiple types of wave movement. The project will also study wave energy converter farms to understand the influence of constructive and destructive interference between devices on power production.
Investigator: Maha Haji, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
Creating Structure-Induced Passive Daytime Radiative Cooling Textiles
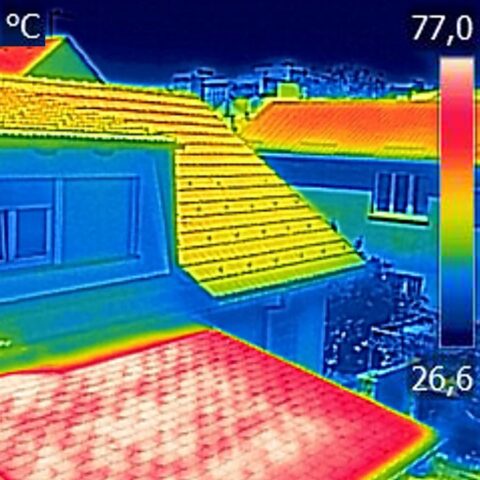
Heat waves have caused more fatalities in the United States than any other weather-related event, and in the past 30 years as the climate has warmed, heat-related deaths in the U.S. have more than doubled. Cornell researchers will build on a fabric surface modification plasma technique they developed to create radiative passive cooling textiles from natural fibers that can be used in indoor and outdoor spaces and in clothing. They will test the scale-up of these cooling textiles with industry partners.
Investigator: Larissa Shepherd, Human Centered Design
Energy-efficient Communication for AI Using Optical Network Fabrics

The rapid expansion of artificial intelligence is consuming huge amounts of energy. One major area of inefficiency is communication bottlenecks between graphics processing units (GPUs). Cornell researchers will design light-based, optical network fabrics that enable faster communication between GPUs and bypass bottlenecks caused by slower electrical connections.
Investigators: Rachee Singh, Computer Science; Emaad Manzoor, Marketing and Management Communication
CO2 Reduction Nanocatalysts in Action
Energy conversion strategies, like splitting water into clean hydrogen or carbon dioxide conversion into liquid fuels, require efficient catalysts to speed electrochemical reactions. Electrochemical reduction of CO2 is especially important for global researchers interested in capturing and reusing CO2. Cornell researchers seek to design a family of nano-scale catalysts that could drive CO2 reduction reactions, and record reactions in real-time using advanced electron microscopes.
Investigators: Yao Yang, Chemistry and Chemical Biology; Erik Thiede, Chemistry and Chemical Biology
2023
Designing Research Solar Farms to Accelerate Sustainable Solar Development

Researchers will develop demonstration projects for agrivoltaic systems, which co-locate solar and agriculture. They intend to create an anchor research solar farm on the Cornell campus to enable comparisons among different solar site configurations – a major gap in agrivoltaic research. This project will engage a professional engineering firm to work with Cornell researchers on a practical and innovative design for a research solar farm that serves Cornell research needs and complies with related regulations and safety standards. They will also explore the feasibility of creating research solar farms at various off-campus facilities on Cornell land.
Investigators: Max Zhang, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering; Harold Van Es, School of Integrative Plant Science; Justine Vanden Heuvel, School of Integrative Plant Science; Sarah Carson, Cornell Campus Sustainability Office
Changes in Shipping Emissions as Natural Analogues for Climate Intervention

Researchers seek to detect changes in surface climate due to novel regulations (from 2020) affecting the amount of sulfate in shipping fuels. This reduction has affected cloud nucleation and resulted in less cloud coverage, especially over the North Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. This has led to questions around the potential for these policies to have affected numerous weather systems in the last two years, such as El Niño and fire conditions in Canada. This project will leverage various observations and large collections of climate model simulations for better clarity. These findings should have broader implications about climate-altering regulations to better inform policymakers and the public.
Investigator: Daniele Visioni, Earth and Atmospheric Sciences
Enabling Clean and Efficient Energy Conversion From Carbon-neutral and Locally Available Fuels

One challenge in the global transition to carbon-neutral renewable energy is the underutilization of low-and carbon-free fuels, including landfill and sewage gas, hydrogen, ammonia, and ultra-lean mixtures of conventional fuels. Waste gases and bio-derived fuels, for example, vary significantly in chemical composition and impurities depending on source and production process, which can lead to reduced operability and unpredictable emissions. Development of robust, fuel-agnostic burners could allow for widespread adoption of alternative fuels. Using advanced porous burners, researchers aim to facilitate clean and efficient energy conversion from nearly any locally available fuel source.
Investigator: Sadaf Sobhani, Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering
Symposium on Accelerating Project Approvals through Updating New York City’s Traffic Analysis Methods

The Jacobs Urban Tech Hub will partner with the NYC Mayor’s Office in hosting and facilitating a symposium with transportation officials and experts on accelerating the approval of city-led and large-scale projects. The focus will be on overhauling traffic analysis methods, which the Mayor has identified as the largest single source of approval delay, regularly adding six months to a year. This event is an outgrowth of the researchers’ Urban Tech Fellowship project investigating opportunities to streamline and automate environmental reviews using up-to-date technologies. Based on the proceedings, the team will author a recommendations report and plan-of-action for city agencies to implement updated traffic methods for official processes, including New York’s City Environmental Quality Review.
Investigators: Michael Samuelian, Director of Jacobs Urban Tech Hub at Cornell Tech; Paul Salama, Jacobs Urban Tech Hub; Anthony Townsend, Jacobs Urban Tech Hub
Methanotrophic Biofilters for Mitigating Methane Emissions From Abandoned Oil and Gas Wells

Fugitive methane emissions from abandoned oil and gas wells are a major source of methane emissions. The U.S. Bipartisan Infrastructure Law has allocated substantial funds to address abandoned well emissions, but due to the expense of well plugging, these funds will address just a small fraction of the problem. Researchers will develop passive biological methane-oxidizing filters that can be used as low-cost and readily-scalable technologies to sustainably mitigate methane emissions from abandoned wells. This research will combine laboratory experiments with field-based measurements of abandoned wells in western New York to produce a proof of concept for the use of methanotrophic biofilters.
Investigators: Matthew Reid, Civil and Environmental Engineering; Ruth Richardson, Civil and Environmental Engineering; Jason Oliver, Animal Science
Forest Farms for Climate Resilient Ecosystems in the Colombian Amazon

Researchers will assess the impacts of Colombia’s climate policy to incentivize 1.2 million hectares of agroforestry and forestation restoration, in collaboration with grassroots farming organizations in the Colombian Amazon. Using innovative bioacoustics and machine-learning technology, they will compare biodiversity between forest sites, cattle ranches, and mixed agroforestry systems growing native products such as cacao, açai, copoazú, and rubber. Understanding how large-scale agroforestry projects transform the landscape of the Colombian Amazon is vital to developing the sustainable farms, food and societies of the future.
Investigator: Stephen Morreale, Natural Resources and the Environment
Ensuring Reliability in the Energy Transition

Increasingly extreme weather events are already challenging the capacity of electricity supplies nationwide. While renewable energy sources are adding capacity to power grids, there is a need for improved market mechanisms and government regulations to ensure reliable, affordable, clean electricity. Researchers are leading a project to elucidate the operational and market issues underpinning electrical resource management and design mechanisms that can facilitate a secure, economically efficient transition to clean energy.
Investigators: Jacob Mays, Civil and Environmental Engineering; Andreea Minca, Operations Research and Information Engineering
Harnessing the Power of Electrochemistry to Upgrade CO2 to Pharmaceuticals
Researchers intend to spearhead new technologies that efficiently harness CO2 as an abundant and sustainable carbon source product to generate valuable pharmaceutical building blocks, including amino acids and carboxylic acids. Researchers with expertise in electrochemical synthesis will collaborate with industrial partner Snapdragon, which specializes in continuous-flow production of pharmaceuticals, to translate their laboratory discoveries into industrial processes that can be immediately adopted by the chemical and pharmaceutical industries. If successful, this approach will not only offer a scalable solution to CO2 utilization but will also help improve the sustainability of pharmaceutical target production.
Investigator: Song Lin, Chemistry and Chemical Biology
Preserving Public Health Amid Environmental Crises

Researchers will develop a public health surveillance system linked to climatological triggers, like heat and cold waves, as climate change worsens the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events and threatens to strain public health resources. They will identify the health syndromes and environmental conditions that should be included in such a system, and create a computational model that takes into account a community’s strengths and vulnerabilities – such as the number of institutional living facilities with highly vulnerable populations, number and location of cooling centers and healthcare capacity.
Investigators: Nathaniel Hupert, Weill Cornell Medicine; Angeline Pendergrass, Earth and Atmospheric Sciences; Flavio Lehner, Earth and Atmospheric Sciences; Arnab Ghosh, Weill Cornell Medicine
Mapping Global Emissions From Food and Agriculture

Understanding the greenhouse gas, land and water use, and economic impacts of the food and agriculture sectors can enable both consumers and policymakers to make better choices for the long-term health of people and the planet. Researchers are updating and expanding a global dataset of livestock production and greenhouse gas emissions developed by Mario Herrero in 2013, to include global emissions from livestock, crops, and aquaculture. This will provide a more realistic representation of the resource use and impacts of food production.
Investigators: Mario Herrero, Global Development; Carlos Gonzalez Fischer, Department of Global Development; Joe Rudek, Environmental Defense Fund
Building a NYS Circular Construction Economy: A Policy Action Plan

The built environment is the world’s largest producer of emissions and waste. Circular construction efforts – such as deconstruction and reuse – present promising alternatives but face many barriers to adoption, including the absence of marketplace infrastructure and policy that would discourage destructive practices and incentivize sustainable alternatives. This project will convene a cross-disciplinary team of academic researchers and industry and community experts to write an actionable white paper to inform groundbreaking deconstruction, salvage, and reuse legislation for New York state. It also could serve as a model for the U.S. and could fuel a circular construction economy.
Investigators: Felix Heisel, Architecture; Jennifer Minner, City and Regional Planning; Lori Leonard, Global Development; Denise Ramzy, Dyson School
Advancing Electrolyzer Technology for Greenhouse Gas Mitigation With Agricultural Anaerobic Digesters

This project aims to advance an innovative electrolyzer technology for mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Using electrochemistry, researchers will convert carbon dioxide into some of the essential buildings blocks for creating pharmaceuticals. By converting biogas from an environmental liability into a source for chemical products, this technology represents a crucial stride in turning scientific progress into practical climate solutions. The researchers aim to prove the technology by demonstrating successful operation with real-world biogas sources. This will facilitate potential follow-on support from external funding and strategic partnerships. This opportunity leverages Cornell’s interdisciplinary research strengths to propel sustainable energy technology.
Investigators: Tobias Hanrath, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering; Héctor Abruña, Chemistry and Chemical Biology; Pete Wright, Animal Science; Lauren Ray, Animal Science; Jefferson Tester, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering; Jillian Goldfarb, Biological and Environmental Engineering
Assessing the Roles of Industrial Policy and Trade Policy in the Market for Renewable Energy

The purpose of this project is to study the potential of industrial policy to help or hinder climate change mitigation efforts. Researchers will develop an inventory of current and former renewable energy subsidies around the world, based on publicly available data from governments and international organizations. They will assess the stated goals of renewable energy subsidies as compared to their actual impacts by surveying academic literature and analyzing news sources. They will then develop policy recommendations that could reconcile the stated and actual impacts of such subsidies and guide institutions in responding to disputes over industrial policy related to renewable energy.
Investigator: Todd Gerarden, Dyson School
Expanding Weather Data Coverage With Optimization-based Balloon Navigation
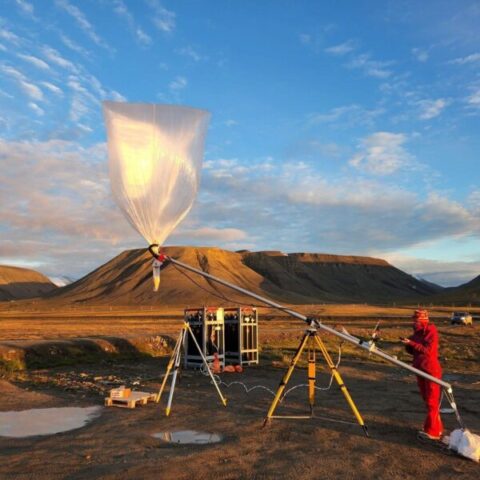

Improving atmospheric data collection addresses both mitigation and prevention aspects of climate change. Weather balloons are an important sensing tool, but their coverage is traditionally determined by launch location and wind patterns. This project will develop planning and control algorithms for advanced weather balloon navigation, expanding coverage to less-studied regions. The algorithms developed will contend with major challenges like uncertain wind forecasts and limited actuation budgets. This project will also serve to create a partnership between researchers at Cornell and WindBorne Systems, an advanced weather balloon start-up, where research results will have direct impact.
Investigator: Sarah Dean, Computer Science
Offsetting Methane Emissions With Biological Methane Consumption
Post-industrial human activities have led to unprecedented levels of atmospheric methane, a potent greenhouse gas. This has led to a dangerous feedback loop of global warming melting glaciers, which then release long-frozen forms of methane. In nature, methane is primarily produced by microbes, which is balanced by symbiotic microbes which consume methane. This proposal seeks to understand how we may mitigate methane emissions by investigating an enzymatic step that is shared between microbial methane producers and consumers. The researchers aim to gain molecular-level insight into this enzymatic process, in order to deploy microbe-based solutions to mitigate methane emissions.
Investigator: Nozomi Ando, Chemistry and Chemical Biology
2022
Empowering Students to Lead the Building Decarbonization Effort With Digital Twins

Building decarbonization is an urgent challenge that requires immediate attention to limit the adverse effects of climate change. However, key professions that shape our built environment, such as architectural design and engineering, urban design, and planning, struggle with integrating STEM content across disciplinary divides and do not prepare students for applied, interdisciplinary, and community-engaged challenges. This project will tap into NSF’s Improving Undergraduate STEM Education (IUSE: EHR) funding to develop new urban simulation models, often called digital twins, that allow modelers to see the “bigger picture” of urban scale synergies and allow data-driven design and planning decisions.
Investigator: Timur Dogan, Architecture
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions From Human-made Ponds

Freshwater ponds are globally abundant and they can support climate resiliency, but ponds are estimated to emit ~6-13% of all global methane (CH4) emissions. However, there is potential for management actions to reduce CH4 emissions. In this project, we will test the extent to which solar-powered aerators reduce CH4 emissions from artificial ponds while measuring other possible benefits to the pond ecosystem, including reductions in algal biomass, increased oxygen concentrations, and cooler temperatures. Ultimately, this work could lead to net benefits for landowners and New York State’s carbon budget, by helping to meet the NYS Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (CLCPA) goals, and advancing the potential for carbon crediting to landowners that reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
Investigator: Meredith Holgerson, Ecology & Evolutionary Biology
Microfluidic-accelerated Directed Evolution for Sustainable Rare Earth Separation
Rare earth elements (REE) are critical ingredients of sustainable energy technologies. However, separating individual REE is one of the hardest problems in chemistry—and current separation methods are highly environmentally damaging. Biosorption offers a promising route to environmentally-friendly REE separation. The research team has recently completed a genome-wide survey of biosorption and discovered six groups of bacteria genes that control binding preference for individual REE. They are seeking to build microfluidic evolution devices that will make it possible to rapidly engineer bacteria with a high affinity for individual REE to enable separations.
Investigators: Mingming Wu, Biological & Environmental Engineering; Buz Barstow, Biological & Environmental Engineering; Justin Wilson, Chemistry & Chemical Biology
Building an Equitable, Diverse, & Unionized Green Energy Economy: What Can We Learn from Pre-Apprenticeship Programs?

The transition to a sustainable, green energy economy will create millions of jobs. But there is no guarantee that the jobs will be high-quality or that the transition will be just. Increasingly, labor unions and policymakers are looking to “pre-apprenticeship” programs to help supply well-trained workers for green projects, creating good-paying, community-sustaining jobs, and ensuring equitable access to these jobs for frontline and marginalized communities. This project will examine and create case studies for three existing pre-apprenticeship programs, identify key attributes of successful programs, and offer recommendations for expanding pre-apprenticeships to meet the needs of our future green economy.
Investigator: Lara Skinner, Climate Jobs Institute
Impact of Climate Smart Biofortified Crops on Nutrition and Health Status in Adolescent and Adult Women

Climate change and the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic threaten to undo the little progress that we have made in improving health status among marginalized populations. Most public health programming is directed towards children or pregnant women and ignores women in other life stages. Biofortification is a food-based approach for improving nutrition and health status, with added benefits of climate-friendly and drought resistance traits. Saurabh Mehta and Julia Finkelstein propose to examine their efficacy using a feeding trial with multiple biofortified staples (pearl millet, wheat, and orange flesh sweet potato) to generate initial evidence of benefit for potential inclusion of such sustainable agriculture-based interventions in public nutrition programs in the future.
Investigators: Saurabh Mehta, Nutritional Sciences; Julia Finkelstein, Nutritional Sciences
Abomasal Infusion of Nutritionally Required Nonessential Amino Acids for Evaluation of Energy and Amino Acid Utilization and Productive Efficiencies in Lactating Dairy Cattle

The dairy industry is focused on methane reduction, yet nitrous oxide from overfeeding protein is 10x more potent as a greenhouse gas and little is being done to reduce protein feeding. The researchers have developed a new approach for estimating amino acid requirements and supply for all essential amino acids (EAA) in their nutrition model, the Cornell Net Carbohydrate and Protein System, which has allowed them to reduce the total N intake of cattle and be more precise in formulating EAA and total N to both improve productivity and reduce N excretion. To improve the ability to reduce N intake and enhance milk protein output, they need to investigate the role of nonessential amino acids (NEAA) in high-producing cattle to determine if they can rely on requirements and supply of metabolizable protein to account for those or if they need to start formulating around particular NEAA to improve milk protein efficiency. They propose to do an abomasal infusion study in high-producing cattle to develop a preliminary data set for another grant.
Investigators: Michael Van Amburgh, Animal Science; Dave Barbano, Food Science
Bioreactor Construction to Demonstrate On-the-fly Guide RNA-directed Evolution (OgRE) of Vibrio natriegens for Electrically-supported Growth

This project will construct a device that facilitates the directed evolution of Vibrio natriegens, an extraordinary microbe that can use electricity as a metabolic input and happens to be the fastest duplicating organism on Earth. The goal is to adapt this microbe to growth on an electrode and formate as sole sources of metabolic energy and fixed carbon, respectively, using a novel directed evolution technique termed OgRE. Such a microbial chassis will enable a myriad of applications that address climate change, including the replacement of agricultural inputs to produce carbon-neutral biofuels or animal feeds, or in carbon-negative carbonate biomineralization.
Investigators: Buz Barstow, Biological and Environmental Engineering; Sijin Li, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Seeking Synergistic Opportunities in the Confluence of Soil Health and Urban Agriculture in Circular Bionutrient Systems

Researchers will lead a convening process that engages teams working in NYC and Ithaca on urban and peri-urban horticulture, with the aim of advancing the circular bionutrient economy. The grant will enable farmers, researchers, and extension specialists to visit in fall 2022 field sites in Ithaca and NYC where studies and demonstrations related to soil health innovations are in progress. The convening will enable the group to formulate a strategy to advance the urban and peri-urban circular bionutrient economy by building on the group’s collective experience and ideas. The convening will yield compelling grant proposals to USDA-NIFA, NE-SARE, and other funders.
Investigators: Jonathan Russell-Anelli, Soil and Crop Sciences; Rebecca Nelson, Plant Pathology and Plant Microbe Biology, and Global Development
Assessing the Global Potential of Circular Bionutrient Economy in Peri-urban Areas for Food System Sustainability

This project assesses the global potential for utilizing organic underutilized resources (OURs) to advance the circular bionutrient economy (CBE) in support of a transition to zero-carbon agriculture. The researchers take a spatially explicit approach to investigate the most relevant factors that influence the potential for food production in peri-urban areas that hosts 39% of global population, based on soil production and amendments that bring together OURs through facilitated regional industrial symbiosis. A typology of conditions as they relate to current and potential contributions to sustainable food production will facilitate the identification of entry points for interventions aimed at improving food security and mitigating carbon emissions through CBE.
Investigators: Chuan Liao, Global Development; Rebecca Nelson, Plant Pathology and Plant Microbe Biology, and Global Development
Passive Cooling Textile With Heterogeneous Infrared Transmittance Performance

To keep surfaces cool and reduce energy requirements for cooling, two passive radiative-cooling approaches include reducing the transmittance (T) of energy from incoming sunlight and increasing the T of outgoing energy via thermal radiation (from building/surface). Both phenomena can be achieved by optimizing surface microstructures. This project will create a textile incorporating heterostructures at micro and nano scales to control T in the Infrared spectrum, corresponding to more than half the energy of solar and thermal radiations. Micron diameter fibers with included submicron particles and voids will be produced, characterized and tested using spectroscopy, solar heating and radiative cooling experiments. This textile could be incorporated as a very thin layer onto exterior surfaces, windows, or clothing.
Investigators: Margaret Frey, Human Centered Design; Yong Joo, Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering; Huiju Park, Human Centered Design
Developing Tools to Assist Local Governments in New York to Estimate Greenhouse Gas Emissions Consistently With the Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act
New York’s Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (CLCPA) of 2019 mandates major changes in how to account for greenhouse gases, including emissions from outside of the state if associated with use of fuel within the state, and more accurately reflecting the role of methane as an agent of global warming by comparing methane to CO2 on a 20-year time period. As mandated by law, the NY DEC produced a new CLCPA-compliant greenhouse gas inventory in December 2021. However, to date the state’s guidance to local governments is not consistent with the CLCPA requirements. The researchers will develop simple spreadsheet tools to help local governments and institutions to estimate the greenhouse gas emissions consistent with the CLCPA.
Investigators: Robert Howarth, Ecology & Evolutionary Biology; Roxanne Marino, Ecology & Evolutionary Biology
A Modular Materials Platform for Next-generation Photovoltaics
The vision of this project is to develop a simple, scalable coating that can improve the efficiency of silicon solar cells by harnessing the unique spin physics of molecular materials to capture energy generally wasted as heat. The researchers aim to establish the proof of concept by templating highly stable molecular dyes within modular framework materials to demonstrate systematic control over their properties. This team will prepare a novel family of crystalline nanocolloids with tunable structure and use a set of ultrafast laser spectroscopy tools to understand how the carrier multiplication process – the key to improving solar cells – can be improved.
Investigators: Andrew Musser, Chemistry & Chemical Biology; Phillip Milner, Chemistry & Chemical Biology
A Just Transition for Autoworkers? E-mobility and Restructuring in Transatlantic Comparison

The proposed study compares the restructuring strategies and worker outcomes associated with the shift toward e-mobility in the U.S. and German auto industries. Automakers are phasing out internal combustion engines and ramping up electric vehicle production, incentivized by regulations and subsidies. This affects millions of workers worldwide. How are these changes managed in contrasting companies and countries? What new approaches are unions, managers, and policymakers developing to mitigate disruption to workers? Using international-comparative mixed-methods research, the researchers will identify best-practice models for managing the transition to e-mobility in a just and equitable way.
Investigators: Ian Greer, ILR Ithaca Co-Lab; Virginia Doellgast, Global Labor and Work
High-Efficiency Electro-Swing Carbon Capture Using Redox-Active Organic Polymers

New materials for carbon dioxide capture from point sources and the air are needed to fight climate change. One of the major limitations of current technologies is the high energy costs required for CO2 desorption. Here, the researchers propose to develop a new class of adsorbents in which electricity can be used instead of heat or vacuum to recover CO2 for subsequent storage or conversion into value-added products. Given the novelty of this multidisciplinary strategy, seed funds are requested to facilitate the collection of preliminary data for a competitive proposal to the DOE or NSF. The completion of this research project would lead to a next-generation family of low-cost, high-efficiency materials for CO2 capture.
Investigators: Phillip Milner, Chemistry & Chemical Biology; Brett Fors, Chemistry & Chemical Biology; Héctor Abruña, Chemistry & Chemical Biology
Carbon Capture at Carbon: New Nucleophiles for Direct Air Capture of CO2

Direct air capture (DAC) of carbon dioxide (CO2) is required to achieve net-negative greenhouse gas emissions. However, current DAC strategies have focused on adapting centuries-old technologies such as aqueous amine and hydroxide solutions. This team will develop new, highly reactive carbon-based molecules capable of DAC for the first time. The project will open up a new class of molecules capable of removing CO2 from humid air, broadening the scope of systems capable of achieving negative emissions. This will enable exciting cross-campus collaborations with the engineering college as the researchers translate the molecules from the laboratory to industrial scale.
Investigators: Tristan Lambert, Chemistry and Chemical Biology; Phillip Milner, Chemistry and Chemical Biology
Conversation for Conservation: The Value of Conversation for Decreasing Lawn Care Maintenance Practices that Harm Bird Habitat

Use of gas-powered tools to maintain residential lawns minimizes and harms bird habitat and contributes extensive GHG emissions. Yet, changing property owners’ lawn care practices has proven difficult due to normative, logistic, legal, and economic factors. Based on emerging research suggesting that conversation in families, among friends, and in neighborhoods is effective in increasing pro-environmental attitudes and intentions, the researchers will examine whether conversation can influence lawn care practices. They will target behaviors that property owners can feasibly change, given the previously mentioned factors. Through a survey and a follow-up experiment, they will study the impact of conversation, especially in groups, on reducing use of gas-powered lawn tools among private property owners in NYS.
Investigators: Poppy McLeod, Communication; Tina Phillips, Cornell Lab of Ornithology; Becca Rodomsky-Bish, Cornell Lab of Ornithology
Advancing Energy-Efficient Hybrid Pathways for Accelerated Carbon Removal

The world’s agricultural soils have lost the carbon equivalent to at least 487 gigatons of CO2. This project aims to develop innovative and economic pathways to rapidly increase soil carbon while harnessing synergistic bio-geo-chemical feedbacks and address the challenge of putting carbon back into the soils to enhance crop fertility. Rapid increases in carbon drawdown require the synergistic coupling of several natural and engineered strategies. Researchers will investigate the coupled influences of enhanced weathering, biochar use, and genetic engineering of plants for enhanced soil carbon storage coupled with distributed processing of bio-waste to co-produce H2, biochar, and carbonates to transform carbon farming.
Investigators: Greeshma Gadikota, Civil & Environmental Engineering; Benjamin Houlton, Ecology & Evolutionary Biology; Yiqi Luo, School of Integrative Plant Science; Johannes Lehmann, Soil & Crop Sciences; Daniel Buckley, Soil and Crop Sciences
